Types of Hearing Loss and Common Causes
 In the most recent nationwide survey in the Philippines on hearing disability and ear disorders conducted by Better Hearing Philippines, Inc., (2005 Martinez et.al.) the prevalence of hearing disability was established at 8.8% of the general population. Furthermore, hearing disability was found to be the 2nd highest form of disability next to moving disability. Hearing loss has become a very common health problem throughout the world. There are four main types of hearing loss, the information below will help you understand those types as well as inform you about common causes for each one.
In the most recent nationwide survey in the Philippines on hearing disability and ear disorders conducted by Better Hearing Philippines, Inc., (2005 Martinez et.al.) the prevalence of hearing disability was established at 8.8% of the general population. Furthermore, hearing disability was found to be the 2nd highest form of disability next to moving disability. Hearing loss has become a very common health problem throughout the world. There are four main types of hearing loss, the information below will help you understand those types as well as inform you about common causes for each one.
There are four types of hearing loss:
- Sensorineural: the most common type of hearing loss, resulting from damage to the inner ear or to nerves within the inner ear
- Conductive: results from problems with ear canal, eardrum, or middle ear
- Mixed: a combination of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss
- Central: an uncommon type of hearing loss that stems from problems within the central auditory system
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural loss is the most common kind of hearing loss. When the tiny hair cells within the inner ear are damaged, those hair cells are unable to provide the required signals to the brain. With this type of hearing loss, sound is able to get to your inner ear normally, but those damaged hair cells send a distorted message of sound to your brain, diminishing your ability to hear.
Common Causes of Sensorineural Hearing Loss:
- Age (also called presbycusis)
- Trauma to the head
- Prolonged exposure to loud noise (This is preventable with proper hearing protection devices)
- Chemotherapy
- Hereditary
- Malformation of the inner ear
- Virus or Disease
There is no known medical cure to reverse sensorineural hearing loss. However, the loss can be helped with amplification devices such as hearing aids, which enable the remaining healthy hair cells to work as efficiently as possible.
Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss occurs when there is a mechanical breakdown in the transmission of sound to the brain. This is usually the result of physical problems with the middle and/or outer ear. Causes of conductive hearing loss can be as simple as a build-up of earwax or as serious as an infection of the middle ear. Other potential causes include dislocation of the middle ear bones or a punctured eardrum. According to the study by Better Hearing Institute of the Philippines, wax problems, otitis media and non-infectious conditions are the leading cause of hearing impairment in the Philippines.
In contrast to sensorineural hearing loss, many cases of conductive hearing loss are able to be corrected with medical treatment or surgery. Often, they may require hearing aids for only a short period of time during recovery, if at all. Cases of conductive hearing loss that aren’t able to be correctly medically can often be successfully treated with hearing aids.
Mixed Hearing Loss
Sometimes hearing loss is the result of multiple factors. When a combination of sensorineural and conductive hearing loss issues are present, it is referred to as mixed hearing loss. Treatment of mixed hearing loss varies for each unique situation. Our staff at Bohol Hearing Clinic can help you to determine the best treatment for mixed hearing loss.
Central Hearing Loss
Central hearing loss is the rarest of the four types of hearing loss. In this type, sound is successfully transmitted through the ear to the brain, but a problem in the central auditory system of the brain limits the individual’s ability to process speech and sound. This is also referred to as an auditory processing disorder. Unfortunately, hearing aids are not able to help with this type of hearing loss. At Bohol Hearing Clinic we are able to provide the Auditory Brainstem Response test that can identify if this is the type of hearing loss you are experiencing.
What are the degrees (levels) of hearing loss?
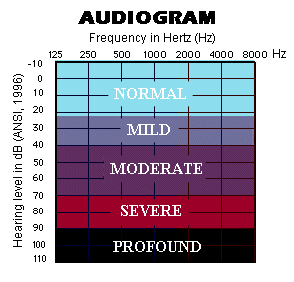
Degrees of Hearing Loss
Generally, the degree of hearing loss is described using one of the five categories:
Mild (average from 25 – 40 dbHL)
Moderate (average from 45 -60 dbHL)
Moderately Severe (average from 60-75 dbHL)
Severe (average from 75 -90 dbHL)
Profound (average above 90dbHL)
